The Ear infection (Otitis), are much more common than we might imagine and can affect both children and adults. They cause intense pain, discomfort, and in some cases, even temporary hearing loss. Those who have experienced it know how difficult it can be to deal with the pain and discomfort of an ear infection.
Understanding what causes otitis, the different types, and how to treat it is essential for maintaining auditory health and preventing future complications. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know to protect your ears and keep your hearing in good shape!

📜Contents
- 1 Ear Infections (Otitis) 🧏♀️
- 2 What Is an Ear Infection (Otitis)? 🤔
- 3 Types of Otitis ⚠️
- 4 What Causes Ear Infections (Otitis)? 📌
- 5 Symptoms of Ear Infection (Otitis) 🤒
- 6 Diagnosing Otitis 🧬
- 7 How to Treat Ear Infections (Otitis) 👨⚕️
- 8 100% Natural Supplement For Ear Infections (Otitis) 🍃
- 9 Preventing Ear Infections (Otitis) 🛡️
- 10 Possible Complications ❤️🩹
- 11 Conclusion 💥
- 12 Also Read – More Posts 💡
Ear Infections (Otitis) 🧏♀️
Ear infections, also known as otitis, are one of the most common complaints, especially among children. Otitis can cause significant discomfort and, if not treated properly, can lead to more serious complications. Auditory health is essential for our overall well-being, as the ear not only allows us to hear but is also involved in our body balance.
When an infection affects the ear, it can impact our quality of life, from difficulty hearing to intense pain. Therefore, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of otitis is key to keeping our ears healthy.
What Is an Ear Infection (Otitis)? 🤔
Otitis is an inflammation or infection that can affect different parts of the ear: external, middle, or inner. It is usually caused by viruses or bacteria that reach the ear through respiratory infections or direct contact with water. Depending on where the infection occurs, otitis can be external, middle, or inner.
Each type has its own causes, symptoms, and treatment options, but the goal is always the same: to relieve pain and prevent major complications such as hearing loss.

Types of Otitis ⚠️
External Otitis (Outer Ear Infection)
- External otitis, also known as “swimmer’s ear,” is an infection that occurs in the outer ear canal, the part that connects the outside of the ear to the eardrum. This type of infection is very common in people who spend a lot of time in the water, such as swimmers. Water retained in the ear canal creates a conducive environment for bacteria and fungi to grow. Symptoms include ear pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, and in more severe cases, pus discharge. Fortunately, external otitis can be easily treated with topical medications and basic hygiene care.
Middle Otitis (Middle Ear Infection)
- Middle otitis occurs in the middle ear cavity, behind the eardrum, and is often caused by colds, flu, or allergies. When the nose and throat become inflamed, fluid can accumulate behind the eardrum, providing fertile ground for bacteria and viruses. Symptoms include sharp pain, fever, irritability (especially in children), and in some cases, fluid discharge. If left untreated, middle otitis can cause complications such as eardrum perforation and temporary or permanent hearing loss. In many cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics and painkillers to treat the infection.
Inner Otitis (Labyrinthitis)
- Inner otitis, also called labyrinthitis, affects the inner ear, the part responsible for balance and hearing. This type of infection is rarer but can have more severe symptoms, such as vertigo (a feeling of intense dizziness), loss of balance, nausea, and in severe cases, hearing loss. Labyrinthitis can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, and treatment includes the use of medications to relieve symptoms and, in some cases, antibiotics or antivirals. Since it directly affects balance, inner otitis can greatly impact daily life, making even simple tasks difficult to perform.
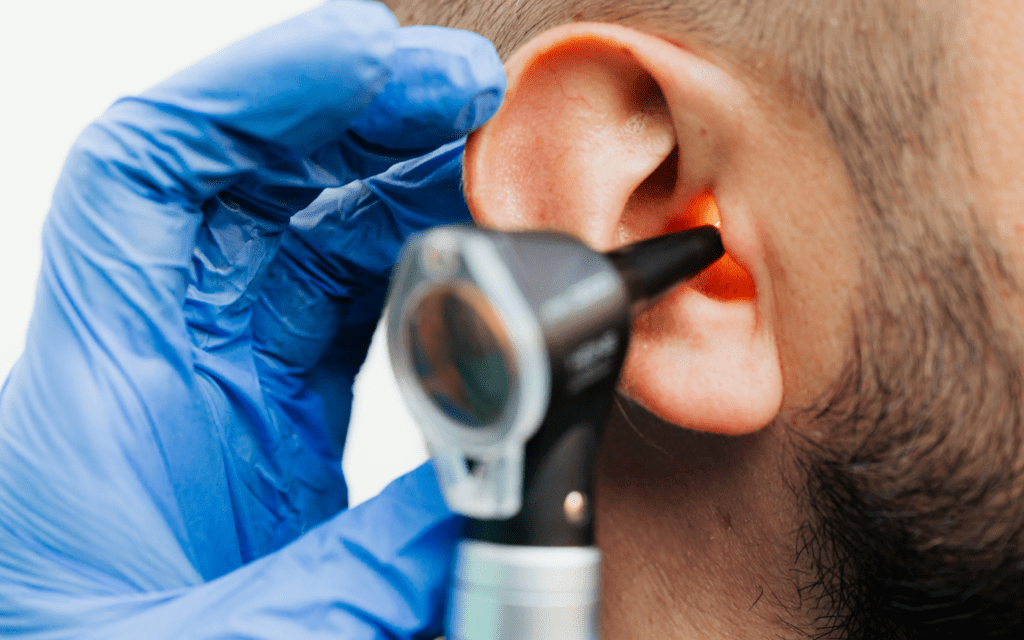
What Causes Ear Infections (Otitis)? 📌
Bacterial and Viral Infections
Ear infections can be caused by both bacteria and viruses. Respiratory infections such as colds and flu can cause inflammation in the upper airways, which spreads to the middle ear, causing otitis. Bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are the main culprits of bacterial otitis.
Viral infections, on the other hand, tend to cause inflammation and fluid accumulation in the ear, creating an ideal environment for bacterial growth.
Allergies and Inflammations
Seasonal or food allergies can trigger inflammation in the nasal passages and ears, facilitating the development of otitis. This happens because allergies cause swelling in the mucous membranes and block the Eustachian tubes, which are responsible for draining fluids from the middle ear.
When this drainage is interrupted, fluid accumulates, increasing the risk of infection.
Environmental Factors
Humid environments, such as pools and beaches, increase the risk of external otitis because water can get trapped in the ear canal, facilitating the proliferation of microorganisms. Additionally, prolonged exposure to pollutants or smoke can irritate the respiratory tract and favor infections in the middle ear.

Symptoms of Ear Infection (Otitis) 🤒
Ear Pain
- Ear pain is the most common and uncomfortable symptom of otitis. It can range from mild to intense and is usually described as a throbbing pain or a feeling of pressure inside the ear. The pain tends to worsen at night when lying down due to increased pressure in the middle ear.
Temporary Hearing Loss
- In many cases of otitis, fluid accumulation or inflammation can block the ear canal, resulting in temporary hearing loss. This hearing loss is reversible after treatment, but it can cause discomfort and impair communication during the infection.
Fever and General Discomfort
- In more severe infections, especially in children, fever may be present, accompanied by general discomfort, irritability, loss of appetite, and difficulty sleeping. These symptoms indicate a more intense infection that requires medical attention.

Diagnosing Otitis 🧬
Physical Ear Examination
A physical examination performed by a doctor is the main way to diagnose otitis. Using an otoscope, the doctor examines the ear canal and eardrum for signs of inflammation, redness, or fluid accumulation. This exam is quick and painless but essential to determine the type of otitis.
Hearing Tests and Laboratory Exams
In some cases, especially when there is hearing loss or complications, the doctor may request hearing tests to assess the infection’s impact. Laboratory tests can also be performed to identify the type of microorganism causing the infection and determine the appropriate treatment.

How to Treat Ear Infections (Otitis) 👨⚕️
Antibiotics and Anti-Inflammatories
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial otitis, helping to eliminate the infection. However, it is important to remember that antibiotics are not effective for viral infections. Anti-inflammatories and pain relievers can also be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Home Remedies
Warm compresses can help relieve pain, and staying hydrated is essential to help the body fight the infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can also be used to relieve discomfort.
Surgery (Tympanostomy)
For chronic or recurrent cases, especially in children, the placement of ventilation tubes through a small surgery may be necessary. These tubes help drain fluid accumulated in the middle ear, preventing new infections and improving hearing.

100% Natural Supplement For Ear Infections (Otitis) 🍃
Natural supplements are an effective way to support health gently and without side effects. One example is ZenCortex, which combines over 20 natural plant and mineral ingredients to promote healthy hearing. Free from stimulants or risk of dependence, ZenCortex is indicated for people over 30, offering effective and safe auditory support.
Produced in the USA, it uses high-quality ingredients and was developed based on modern science to naturally optimize your hearing.
Preventing Ear Infections (Otitis) 🛡️
Swimming Precautions
To prevent external otitis, it is important to dry your ears well after swimming and use earplugs when necessary. Avoiding prolonged exposure to humid environments is essential to prevent the growth of bacteria.
Hygiene and Cold Care
Maintaining good nasal hygiene and properly treating colds can help prevent otitis, especially middle otitis. Vaccines against the flu and other respiratory diseases are also effective in prevention.

Possible Complications ❤️🩹
Permanent Hearing Loss
If otitis is not treated properly, especially chronic middle otitis, damage to the eardrum or ossicles in the ear can occur, resulting in permanent hearing loss. This underscores the importance of seeking treatment early in the symptoms.
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is a serious infection that can occur if middle otitis spreads to the mastoid bone located behind the ear. This complication can be dangerous and requires urgent treatment with antibiotics or, in severe cases, surgery.

Conclusion 💥
We have learned what ear infections (otitis) are, what causes ear infections (otitis), symptoms of ear infection (otitis), how to treat ear infections (otitis), prevention, and much more.
Taking care of auditory health is essential to avoid the pain and discomfort caused by ear infections (otitis). Pay attention to your body’s signals because ear pain, temporary hearing loss, or even fever can indicate that something is wrong. If these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical help and follow treatment guidelines. With the right care, it is possible to avoid complications and keep your ears healthy and protected!
Also Read – More Posts 💡





[…] Ear infection (Otitis): What is it, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments ✅ […]
[…] Ear infection (Otitis): What is it, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments ✅ […]
[…] Ear infection (Otitis): What is it, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments ✅ […]